 | |
|
|
Pretest 3.2
- TRUE? Or FALSE?
- A system at equilibrium is closed. True.
- The equilibrium reactants are completely transformed into products. False
- For a system to remain at equilibrium, the temperature must remain constant. True
- Equilibrium reactions are reversible. True
- The macroscopic properties of an equilibrium system remain constant. True
- In a steady state the input rate equals the output rate. True
- In a reaction at equilibrium the forward rate is greater than the reverse rate. False
- Every time a cerebral character (happy face) befriends a romantic (heart), a cerebral-romantic couple(heart stuck to face) break up.
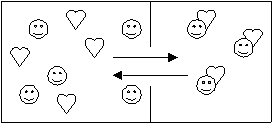
![]()
- In two years, how many couples will there be if this system remains at equilibrium? (see diagram)
- Write an equation to represent the equilibrium.
3 (no change)
Happy face + heart = happy-heart
3. Write an equilibrium law expression for the following reaction:
2 H2O(g) + 2 S(s) = 2 H2S(g) + O2(g)
![]() ( notice solid sulfur is purposely left out)
( notice solid sulfur is purposely left out)
4. What chemical equation is represented by the following?
![]()
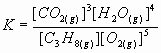
C3H8(g) + 5 O2(g) = 3 CO2(g) + 4 H2O(g)
5. At equilibrium [NO 2(g)] = 3.0 M and [N2O4(g)] = 4.0 M. Calculate the equilibrium constant, K.
2 NO 2(g) = N2O4(g) + energy
![]()
6. a. In a 5.0 L flask, 3 moles of oxygen are introduced with 8 moles of iodine. At equilibrium we find 1.0 mole of oxygen among the other chemicals. Find K.
O2(g) + 2 I2(g) = 2 OI2(g)
|
|
O2(g) |
I2(g) |
OI2(g) |
|
initial number of moles |
3 |
8 |
0 |
|
moles reacting/forming |
3-1 = 2 |
I2/O2 = 2, so 2(2) = 4 |
OI2/O2 = 2, so 2(2) = 4 |
|
Moles at equilibrium |
1 |
8-4=4 |
4 |
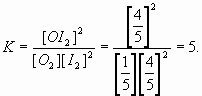
- If temperature is raised and K is found to be a lower value, then is the reaction endothermic?
No it is exothermic; otherwise, K would have been higher.
7. Given: 4 HCl(g) + O2(g) = 2H2O(g) + 2Cl2(g) + 112kJ
At a certain temperature, the equilibrium constant for the above reaction is 32.
There were no products initially and the following equilibrium concentrations were measured. [HCl] = 2.0 M [O2] = 2.0 M
What are the equilibrium concentrations of steam and chlorine?
Let x = [H2O] = [Cl2], since there were no products initially.
| 2H2O | 2Cl2 | |||
| initial | doesn't matter | 0 | 0 | |
| reacting/forming | doesn't matter | x(ratio steam to chlorine is 2:2 or 1:1) | x | |
| equilibrium | 2 | 2 | x | x |
![]()
![]()
x4 = 210
x = (210)1/4
x = 2 2.5 = 5.65 M
8. Given: X(g) + Z(g) = XZ(g) K = 9.0 at 300 C.
If we introduce 2.0 moles of X and 2.0 moles of Z into a one litre flask, how many moles of XZ, X and Z will be found at equilibrium?
|
|
X(g) |
Z(g) |
XZ(g) |
|
initial number of moles |
2 |
2 |
0 |
|
moles reacting/forming |
x |
x |
x |
|
Moles at equilibrium |
2-x |
2-x |
x |
![]()
9x2 - 36x + 36 - x = 0
9x2 - 37x + 36 = 0.
x = 1.58 or 2.53. But x<2, so [XZ] =1.58 M and [X] = [Z] = 2-1.58 = 0.42 M.
9. Does a catalyst affect the value of K? Explain.
No. A catalyst only allows equilibrium to establish itself faster.
10. At equilibrium , stronger acids have far more H+1 than weaker acids.
HX(aq) = H+1(aq) + X-1(aq)
Which, then, is the most reasonable K value for a very weak acid? ( all K values are in mol/L)
A. 1.2 X 10-22
B. 1.2 X 10-1 C 1.2 X 102 D 1.2 X 1022