Rates and Nature: A Closer Look
1. In chloroplasts plants use photosynthesis to convert water and carbon dioxide into sugars and oxygen. The overall reaction is:
n CO2
+ 2n H2O à [Cn(H2O)(n-1)] + n O2 + (n+1)H2O
sucrose if n = 12, or starch if n = large
The sequence of reactions leading up to the above overall reaction is complicated, but it would never happen on its own if the rate was not catalyzed by chlorophyll molecules.
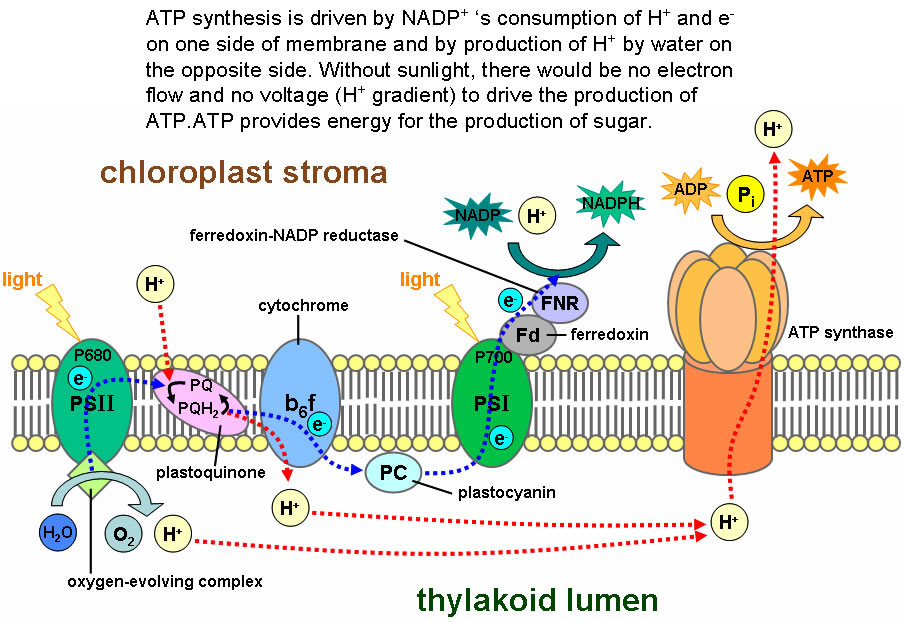
- When light strikes chlorophyll molecules, they lose an electron, which is picked up by a molecule that helps link up CO2 molecules.
- The electron is eventually returned to chlorophyll. The molecule that ultimately loses its electrons for the sake of chlorophyll is water:
2 H2O à 4H+1 + O2 + 4e
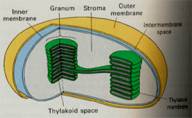
Figure 1 Chloroplast
Note that the above reaction releases oxygen, which is why plants release O2 while growing. The reaction also concentrates H+1 on one side of the membrane in those little green disks shown in Figure 1. That allows an energy carrying molecule, ATP, to be made, and the energy is invested in the production of sugars.
· Note, that after all is said and done, chlorophyll is available again to absorb more light, and to start the whole cycle again. True catalysts speed up reactions without being consumed.
2. Enzymes, as we have seen, are biochemical catalysts. Without them there would be no life. They catalyze everything from the synthesis of protein in our skin to the breakdown of all food molecules in our digestive system.
Example: sucrose + enzyme à glucose + fructose + enzyme.
3. In hibernating animals, body chemistry can be altered so that the organism can survive at lower temperatures. This lowers the amount of oxygen and glucose that the hibernator needs.
Rates and Technology: A Closer Look
1. Refrigeration lowers the rate of oxidation (lower temperature), and it makes it difficult for bacteria and mold to reproduce.
2. Preservatives such as BHT in cereal packaging out-compete the cereal for oxygen, which is desirable because food goes stale when it oxidizes. Preservatives, however, are not true inhibitors because they are consumed in the reaction with oxygen.
3. Catalytic Converters use rhodium and platinum to attract the pollutants CO and NO2 onto their surface. These are then broken down according to:
NO2 à N2 + O2
CO + 0.5 O2 à CO2
4, Soaps are mixed with enzymes to breakdown proteins and starch molecules found in stubborn stains.